Member Login for Full Site Content |
|
- Home
- Communities of Interest
- MACRL
- Missouri Librarian AI Resource
- Stakeholders
Stakeholders
Personal Responsibility
Personal Responsibility
-
Consider your own use -- informed use
-
Be aware of: misinformation, reproducibility, information about the tool, your own company/organization's policy
-
-
Link to Limitations page (under Demystifying)
-
-
Acknowledgement of use - this is a webform that can be dropped anywhere for folks to generate an ai acknowledgement example
https://github.com/e3la/ai-acknowledgement/ -
https://app.diagrams.net/?page-id=C5RBs43oDa-KdzZeNtuy&client=1 editable version of this flowchart
AI Tool Acknowledgment Form | This AI flowchart can be useful to communicate essential information literacy skills as they relate to generative AI. By prompting users with critical questions about truth, accuracy, copyright, and personal responsibility, the guide serves to educate individuals on the ethical implications and inherent limitations of AI tools, moving beyond usage to fostering a responsible and discerning approach. It empowers users to make informed decisions by providing a clear framework for evaluating specific AI applications, thereby supporting academic and professional integrity while mitigating potential risks such as misinformation or copyright infringement. Librarians can utilize accessible visual tools to proactively address the challenges of new technologies, positioning the library as a crucial resource for navigating the evolving digital landscape and promoting critical engagement with AI-generated content. The words about this flowchart were generated by Gemini - you can find the prompt conversation (beginning with an XML version of the flowchart) can be found at https://aistudio.google.com/app/prompts?state=%7B%22ids%22:%5B%221G3eWhPNOW1gEOg4_f6ZEydhiSZlB_fMI%22%5D,%22action%22:%22open%22,%22userId%22:%22106660125245618830440%22,%22resourceKeys%22:%7B%7D%7D&usp=sharing Promoting Information Literacy in the AI Age: Just as librarians teach how to evaluate traditional sources, they now need to teach how to evaluate AI-generated content. This flowchart is a practical tool for developing critical thinking skills specifically for AI. It moves beyond simply "using AI" to "using AI responsibly and discerningly." Educating on Ethical AI Use: The flowchart directly addresses ethical considerations like copyright, accuracy, and responsibility. Librarians are often at the forefront of discussions about academic integrity and ethical research. This guide provides clear, actionable steps for users to consider these ethics before and during AI use. Highlighting the Limitations of AI: Many users might assume AI is always correct or can replace human expertise entirely. The flowchart challenges these assumptions by asking crucial questions about truth, verification, and responsibility, thereby setting realistic expectations about AI's current capabilities and limitations. Empowering Informed Decision-Making: Instead of just telling users "don't use AI for X," this flowchart empowers them to make their own informed decisions. It provides a framework for evaluating their specific use case against important criteria, leading to a more nuanced understanding of AI application. Supporting Academic and Professional Integrity: In academic settings, the use of AI raises questions about originality, plagiarism, and proper citation. This flowchart encourages acknowledgment of AI use and careful review, which are vital for maintaining academic and professional standards. Mitigating Risks (Legal, Academic, Personal): By prompting users to consider copyright, accuracy, and responsibility, the flowchart helps them identify situations where AI use could lead to legal issues (copyright infringement), academic penalties (plagiarism, misinformation), or personal harm (acting on inaccurate medical or legal advice). Providing a Clear and Accessible Guide: Flowcharts are excellent visual tools for breaking down complex decision processes into manageable steps. This makes the information more accessible and less intimidating than a lengthy policy document, encouraging wider adoption and understanding. Adapting to Evolving Technologies: Librarians are continuously adapting their services and resources to new technologies. Sharing a guide like this demonstrates a proactive approach to addressing the challenges and opportunities presented by generative AI, positioning the library as a relevant and essential resource for navigating the modern information landscape. Facilitating Discussion and Policy Development: This type of guide can serve as a starting point for broader discussions within an institution (university, school, company) about AI policies, guidelines, and best practices. It helps to frame the critical questions that need to be considered. |
Activities for Educators
These activities are to encourage educators to explore GenAI tools and consider how they can incorporate GenAI into their classes. These activities were utilized from "Exloring GenAI Tools in Higher Education" in the GenAI in Teaching and Learning Toolkit by Gwen Nguyen which is licensed under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 International License.
Activity 1: Mapping the AI Landscape
This activity is designed to deepen educators’ understanding of the broad landscape of AI, highlighting its various subfields and applications. Please continue to develop this conceptual diagram that distinguishes between different AI technologies, as well as list real-world applications or tools you have encountered or used. Objectives:
Instructions:
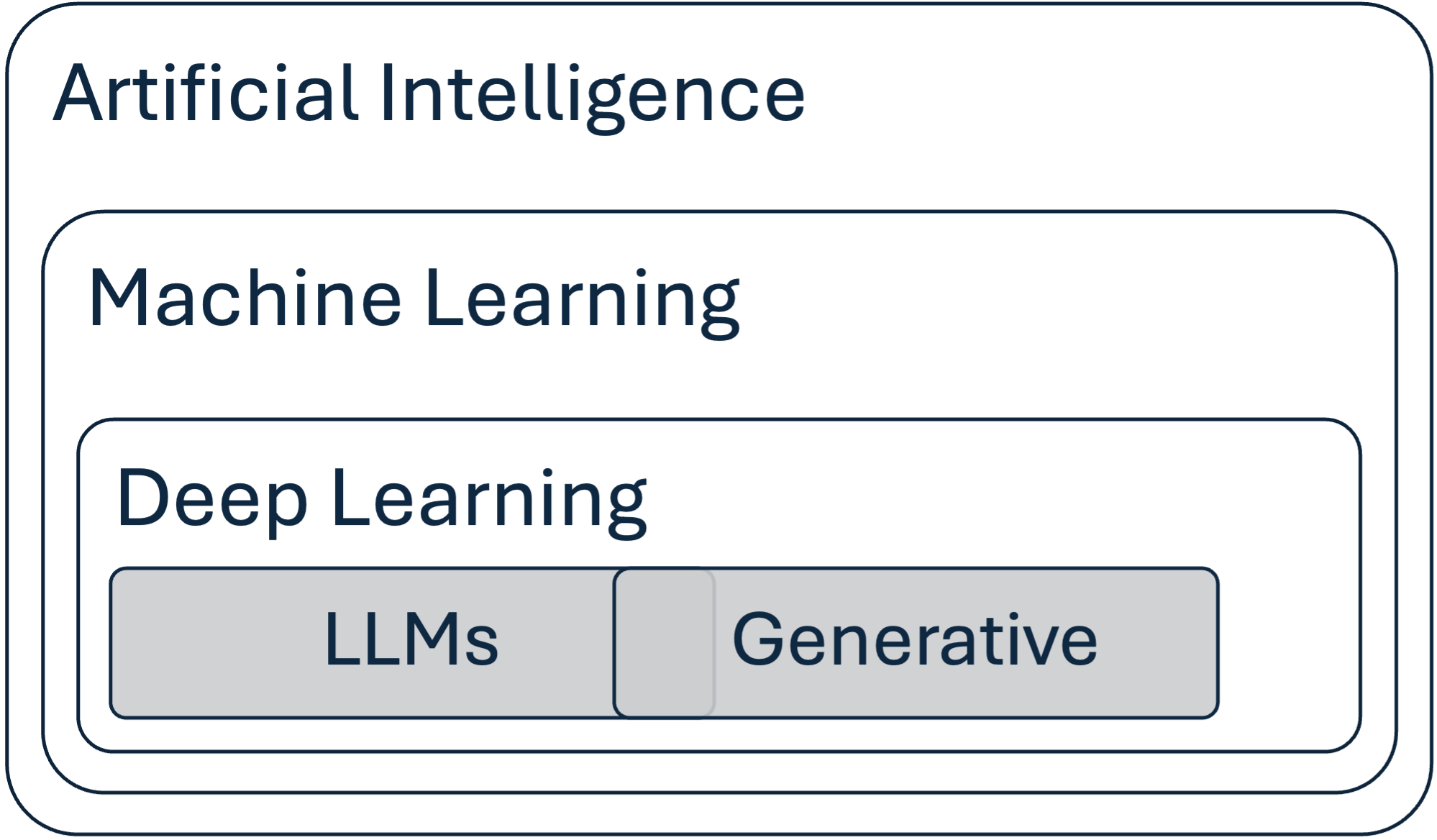
Notes:
Activity 3: GenAI tools BINGO challenge for educators This BINGO worksheet encourages educators to explore various generative AI tools, experimenting with both text-based and image generation platforms. By engaging with these tools, participants can better understand their functionalities, applications, and limitations in educational settings. Instructions:
| Activity 2: Explore various GenAI tools This activity provides educators with the opportunity to interact firsthand with a variety of GenAI tools. Participants engage with these tools through guided exploration, reflecting on their experiences to evaluate the utility and limitations of each tool in educational settings. Objectives:
Instruction: Below are brief introductions to various GenAI tools along with links to their respective platforms. Spend about five to ten minutes with each tool, experimenting with its features and testing its functionalities relevant to your educational context. After exploring each tool, take a moment to reflect on your experience. Consider one of these following questions:
(1) Large language models (LLMs) ChatGPT: ChatGPT is probably the most well-known of the LLMs and it is an extraordinary tool. You can access it with no login, but be sure to save anything valuable you create. You can create a free account that gives you access to GPT4o, which is an extremely powerful model. You can also access GPTs, which are smart AI tools designed for specific purposes. You need a paid account to create your own GPTs. Claude: Claude is a powerhouse AI that’s a great go-to when you need to read or output longer materials. Among its outstanding features are the ability to work with larger uploaded pdfs and the ability to create artifacts, such as code, webpages, SVG graphics, and other interactions. The artifacts capability must be toggled on. With the paid version of Claude, you get access to Projects, which allow you to create continuous workspaces and customize memory and outputs across a project. Microsoft Copilot: Microsoft Copilot is a web-based AI tool that lets you chat, draw, and more. With your institutional credentials, you can access a version of the tool with enhanced privacy protection. It does not save your chat history so be sure to capture anything valuable you create. Gemini: Gemini, the AI model from Google, is a rising star in LLM land. Formerly known as Bard, the model is said to be able to tackle complex tasks. Gemini connects with Google Maps, which can help for certain kinds of tasks. Give it a spin and see what you think. (2) Image generation Firefly: Firefly is a super cool, free program that lets you create and edit images. We love its built-in, selectable filters at the bottom right of your Firefly screen. Even more, we’re super impressed with Abobe’s thoughtful and inclusive practices when it comes to training the model that creates the magic. DALL-E 3: DALL-E is the AI image generator that you access through ChatGPT. The free version creates images, but it can be significantly slower and lower quality than a paid version. Microsoft Copilot: Microsoft Copilot is a web-based AI tool that lets you chat, draw, and more. Once you have an image, you can even do some cool edits in Microsoft Designer if you’re signed in with personal credentials. You can also use Copilot with your institutional credentials and create images, though you may be limited to how many you can create in a day. Ideogram: Ideogram is currently a free online AI image generator. This generator allows you to describe the image you would like to see and then generate it on the website. This website requires you to create a personal account. Other people will be able to see and download any image you create. (2) Other tools Perplexity: Perplexity is an amazing AI-powered research assistant that does an internet search to show you where the information is pulled from and where you can look for more related content. The free basic version is available to everyone. Canva: Canva has a wide range of tools in the area they call Magic Studio, which holds all of their AI-powered design features. It includes presentation generation and text-to-video and text-to-image generators, as well as more powerful photo editing tools. Glasp: Glasp is a Chrome or Safari extension that has tons of cool functionality for note-taking. This tool allows you to capture online content with colored highlights, which are curated on your Glasp homepage. This is a great tool for researchers and students as it allows them to organize notes and highlighted information using tags and authors, as well as track their learning progress and share information with others. Goblin Tools: Goblin Tools is a collection of small, simple, single-task tools designed to help neurodivergent people with tasks that they find overwhelming or difficult. These tools use AI technologies to assist with various functions, such as Magic ToDo that helps break down tasks into manageable steps or Formalizer that assists in converting informal language into formal text. Gamma: Gamma is a subscription-based AI tool that builds presentations and websites for you with just a few keywords. They also have an option to transform existing Word documents and PowerPoint presentations into stunning visual presentations in just a few minutes so you can use what you already have and edit from there. Gamma is free to try, but there are additional pricing tiers to access more features and to renew the number of products you can create each month. Grammarly: Grammarly is an AI-powered writing assistant designed to help users improve their writing by providing suggestions for grammar, spelling, punctuation, clarity, engagement, and delivery. MagicSchool.ai: MagicSchool.ai is an AI-powered platform designed specially for educators to generate rubrics, lesson plans, and other educational materials. There is also a coaching tool, named Raina, that can help educators think through ideas and standards. Diffit: Diffit is a resource builder and marker for class readings and PDFs that educators can use for their class. Students cannot use Diffit and, if teachers use it, they cannot enter students’ personal information. Almanack: Almanack is an AI-powered tool designed to assist educators in creating and managing lesson plans, resources, and assessments. There is a free standard version. Slidesgo: Slidesgo is a platform that offers a wide range of professionally designed templates for creating presentations. With the new AI-enabled features, educators can create presentations in minutes, generate ice-breaker activities, develop assessments for students, and plan some lessons faster. |



.png)